Distributed Denial of Service Attack
A denial-of-service attack (DoS attack) is an attempt to make a computer resource unavailable to its intended users. Although the means to carry out, motives for, and targets of a DoS attack may vary, it generally consists of the concerted efforts of a person, or multiple people to prevent an Internet site or service from functioning efficiently or at all, temporarily or indefinitely. Perpetrators of DoS attacks typically target sites or services hosted on high-profile web servers such as banks, credit card payment gateways, and even root name servers. The term is generally used relating to computer networks, but is not limited to this field; for example, it is also used in reference to CPU resource management.
One common method of attack involves saturating the target machine with external communications requests, such that it cannot respond to legitimate traffic, or responds so slowly as to be rendered effectively unavailable. Such attacks usually lead to a server overload. In general terms, DoS attacks are implemented by either forcing the targeted computer(s) to reset, or consuming its resources so that it can no longer provide its intended service or obstructing the communication media between the intended users and the victim so that they can no longer communicate adequately.
A distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack is one in which a multitude of compromised systems attack a single target, thereby causing denial of service for users of the targeted system. The flood of incoming messages to the target system essentially forces it to shut down, thereby denying service to the system to legitimate users.
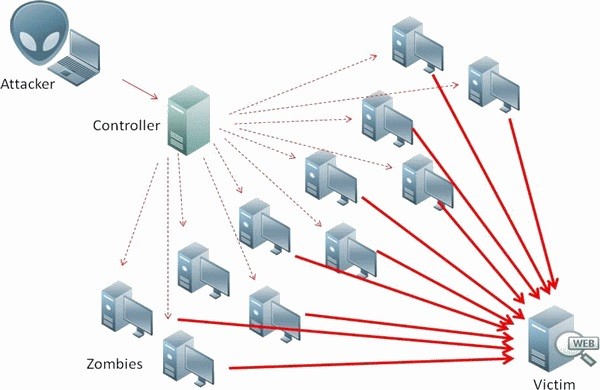
In a typical DDoS attack, a hacker (or, if you prefer, cracker) begins by exploiting a vulnerability in one computer system and making it the DDoS master. It is from the master system that the intruder identifies and communicates with other systems that can be compromised. The intruder loads cracking tools available on the Internet on multiple - sometimes thousands of -- compromised systems. With a single command, the intruder instructs the controlled machines to launch one of many flood attacks against a specified target. The inundation of packets to the target causes a denial of service.
While the press tends to focus on the target of DDoS attacks as the victim, in reality there are many victims in a DDoS attack -- the final target and as well the systems controlled by the intruder. Although the owners of co-opted computers are typically unaware that their computers have been compromised, they are nevertheless likely to suffer degradation of service and malfunction. Both owners and users of targeted sites are affected by a denial of service. Yahoo, Buy.com, RIAA and the United States Copyright Office are among the victims of DDoS attacks. DDoS attacks can also create more widespread disruption. In October 2010, for example, a massive DDoS attack took the entire country of Myanmar offline.

